You Think You Know What Ginger Is? Test Yourself
The Wonder of Ginger: A Comprehensive Guide to Its History, Uses, and Benefits
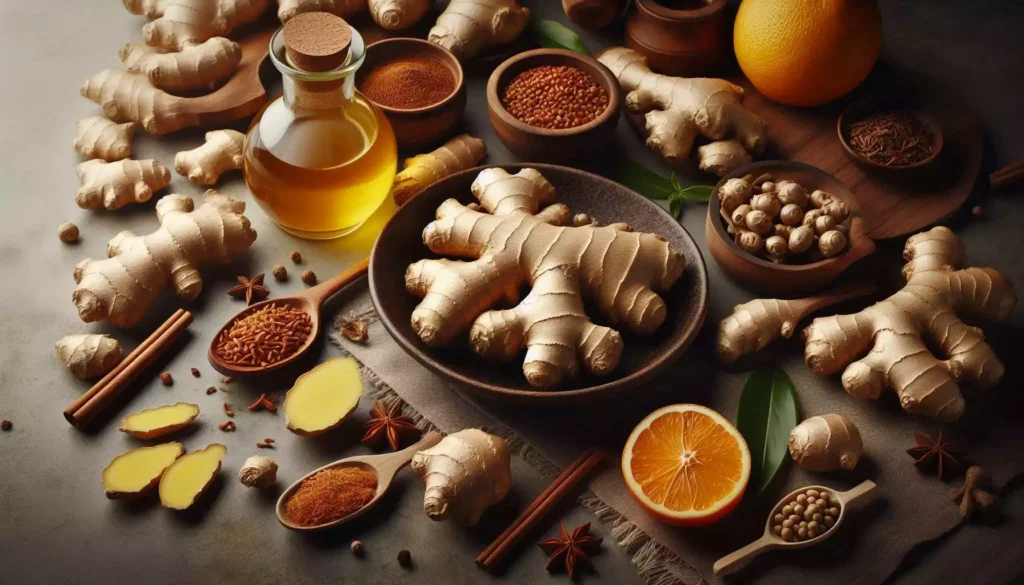
Ginger, a humble root with a fiery personality, has been a staple in cuisines and medicine for thousands of years. Native to Asia, this versatile rhizome has journeyed across the globe, captivating the palates and imaginations of people worldwide. Whether you’re a food enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or simply curious about the wonders of nature, ginger is a subject worth exploring. In this article, we delve into the history, culinary uses, health benefits, and cultural significance of ginger, making it a must-read for anyone looking to learn more about this incredible plant.
You Think You Know What Ginger Is? Test Yourself
The History of Ginger
Ginger’s story begins over 3,000 years ago in ancient China, where it was not only a culinary ingredient but also a medicinal herb and a form of currency. The Chinese valued ginger for its ability to warm the body and balance the energies, according to traditional Chinese medicine. From China, ginger spread to India, where it became a key ingredient in Ayurvedic medicine and a staple in Indian cuisine. By the first century AD, ginger had reached the Mediterranean, where it was prized by the Romans for its flavor and preservative qualities.
The Spice Trade of the Middle Ages further cemented ginger’s place in global cuisine. Arab traders brought ginger to the Middle East and Africa, where it was incorporated into local dishes and used in traditional remedies. By the 16th century, European colonizers had introduced ginger to the Americas, where it quickly became a popular ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes.
Culinary Uses of Ginger
Ginger is a culinary chameleon, capable of transforming dishes with its unique flavor and aroma. Whether it’s grated, sliced, diced, or juiced, ginger adds a zesty kick to a wide variety of recipes. Here are some popular ways to use ginger in the kitchen:
- Baked Goods: Gingerbread, ginger snaps, and ginger cakes are classic examples of how ginger can add warmth and spice to sweet treats.
- Beverages: Ginger tea, ginger ale, and ginger beer are just a few of the many drinks that showcase ginger’s refreshing flavor.
- Savory Dishes: Stir-fries, curries, and soups often rely on ginger for depth and heat. In Asian cuisine, ginger is a fundamental ingredient, alongside garlic and soy sauce.
- Marinades and Sauces: Ginger is a key component in marinades for meats and fish, as well as in dipping sauces and condiments.
- Pickling: Sliced ginger is often pickled and served as a palate cleanser between courses in Japanese cuisine.
For those looking to experiment with ginger in their cooking, here are some tips:
- Fresh vs. Dried Ginger: Fresh ginger has a brighter, more aromatic flavor, while dried ginger is warmer and more concentrated. Choose the form that best suits your recipe.
- Ginger Peel: While the peel is edible, it can be fibrous and bitter. Peel ginger before grating or slicing for a smoother texture.
- Ginger Substitutes: If fresh ginger is unavailable, ground ginger can be used as a substitute in most recipes. However, the flavor will be less vibrant.
Health Benefits of Ginger
Beyond its culinary appeal, ginger has been revered for its medicinal properties for centuries. Modern science has confirmed many of the traditional uses of ginger, making it a natural remedy for a variety of ailments. Here are some of the most significant health benefits of ginger:
- Relieves Nausea: Ginger has been shown to alleviate nausea caused by motion sickness, pregnancy, and chemotherapy. Its anti-inflammatory properties help soothe the digestive system and reduce inflammation.
- Aids Digestion: Ginger stimulates the production of digestive enzymes, helping to break down food and prevent indigestion. It is also known to relieve bloating and gas.
- Reduces Inflammation: Ginger contains compounds called gingerols, which have potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These compounds may help reduce pain and swelling in conditions like arthritis.
- Supports Immune Function: Ginger’s antimicrobial properties make it effective against colds, flu, and other infections. It can also help reduce congestion and soothe a sore throat.
- May Lower Blood Sugar: Some studies suggest that ginger can help regulate blood sugar levels, making it a potential natural remedy for managing type 2 diabetes.
- Improves Heart Health: Ginger has been shown to lower cholesterol levels and prevent blood clots, both of which can contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease.
To incorporate ginger into your health routine, consider the following tips:
- Ginger Tea: Slice fresh ginger thinly and steep it in hot water for 5-10 minutes. Strain and enjoy with honey or lemon for added flavor.
- Ginger Supplements: For those who prefer not to consume ginger raw, supplements are a convenient option. However, consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Ginger Oil: Ginger essential oil can be used in aromatherapy to relieve nausea and improve mood. Always dilute essential oils with a carrier oil before applying to the skin.
Cultural Significance of Ginger
Ginger’s impact extends beyond the kitchen and the medicine cabinet. In many cultures, ginger holds a special symbolic meaning. In Chinese culture, ginger is a symbol of longevity and prosperity, often given as a gift during special occasions. In India, ginger is considered a sacred plant, associated with the god Vishnu. In Japan, pickled ginger is not only a palate cleanser but also a symbol of good luck and longevity.
Ginger has also played a significant role in religious and spiritual practices. In Ayurvedic tradition, ginger is one of the three main herbs used to balance the body’s energies. In traditional Chinese medicine, ginger is used to warm the body and expel cold energies. In many indigenous cultures, ginger is believed to have spiritual cleansing properties, used in rituals to purify the body and mind.
How to Incorporate More Ginger into Your Diet
If you’re looking to make ginger a bigger part of your diet, here are some practical tips to get you started:
- Start Your Day with Ginger: Begin your morning with a glass of ginger water or a cup of ginger tea. This can help kickstart your metabolism and set a positive tone for the day.
- Add Ginger to Your Meals: Grate fresh ginger over soups, stir-fries, and salads for a burst of flavor. You can also incorporate ground ginger into baked goods, marinades, and sauces.
- Incorporate Ginger into Snacks: Sliced fresh ginger can be paired with nuts or dried fruit for a healthy and satisfying snack. Crystallized ginger is another delicious option, offering a sweet and spicy treat.
- Experiment with Ginger in Drinks: Beyond tea and beer, ginger can be added to smoothies, juices, and cocktails. Try making a ginger-based mocktail by combining fresh ginger juice with lime, mint, and sparkling water.
- Store Ginger Properly: To keep fresh ginger fresh for longer, store it in the refrigerator. Wrap it tightly in plastic wrap or place it in a sealed container to prevent drying out.
Conclusion
Ginger is more than just a spice; it’s a treasure trove of flavor, health benefits, and cultural significance. Whether you’re looking to add some heat to your cooking, find natural remedies for common ailments, or explore the rich history of this ancient root, ginger is a subject that offers endless fascination. With its versatility in the kitchen, its proven health benefits, and its deep-rooted place in global culture, ginger is a true wonder of nature that deserves to be celebrated and enjoyed. So next time you reach for the ginger in your pantry, remember the centuries of history, the countless uses, and the incredible benefits that this humble root has to offer.

Certainly! Below are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about ginger, along with their answers:
General Information
Q1: What is ginger?
A1: Ginger is a flowering plant whose rhizome (root) is widely used as a spice and in traditional medicine. It is native to Southeast Asia but is now cultivated in many parts of the world. Ginger is known for its distinctive, pungent flavor and numerous health benefits.
Culinary Uses
Q2: How is ginger used in cooking?
A2: Ginger can be used in various forms in cooking, including fresh, dried, powdered, and pickled. It is commonly used in stir-fries, curries, soups, baked goods, and beverages like tea and ginger ale. Fresh ginger is often grated or sliced, while dried ginger is typically used in powdered form.
Q3: What are some popular dishes that use ginger?
A3: Ginger is a key ingredient in many dishes, including:
- Asian Cuisine: Stir-fries, curries, and marinades.
- Baked Goods: Gingerbread, ginger cookies, and ginger snaps.
- Beverages: Ginger tea, ginger ale, and cocktails.
- Indian Cuisine: Garam masala, chai tea, and various vegetable and meat dishes.
Health Benefits
Q4: What are the health benefits of ginger?
A4: Ginger is known for several health benefits, including:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Helps reduce inflammation in the body.
- Digestive aid: Can help relieve nausea, indigestion, and bloating.
- Pain relief: May help reduce muscle pain and soreness.
- Immune booster: Contains antioxidants that can boost the immune system.
- Anti-nausea: Often used to alleviate morning sickness and motion sickness.
Q5: Can ginger help with nausea?
A5: Yes, ginger is widely recognized for its ability to alleviate nausea. It is often recommended for morning sickness during pregnancy, motion sickness, and post-surgery nausea. Ginger can be consumed in various forms, such as ginger tea, ginger candies, or ginger ale.
Storage and Handling
Q6: How should I store fresh ginger?
A6: Fresh ginger should be stored in a cool, dry place, such as a refrigerator. It can be kept in a plastic bag or airtight container to prevent moisture. Fresh ginger can last for several weeks when stored properly.
Q7: How do I prepare fresh ginger?
A7: To prepare fresh ginger:
- Peel the skin: Use a spoon or a vegetable peeler to remove the outer skin.
- Grate or slice: Grate the ginger using a microplane or slice it thinly using a knife.
- Chop or mince: For some recipes, you may need to chop or mince the ginger finely.
Medicinal Uses
Q8: Can ginger be used in traditional medicine?
A8: Yes, ginger has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. In Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine, it is used to treat a variety of conditions, including digestive issues, colds, and flu. Ginger is also used in herbal remedies and teas.
Q9: Are there any side effects of consuming ginger?
A9: While ginger is generally safe for most people, some individuals may experience side effects, such as:
- Stomach discomfort: Excessive consumption can cause heartburn or diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to ginger.
- Interaction with medications: Ginger can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners, so it’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you are taking any medications.
Growing and Cultivation
Q10: How can I grow ginger at home?
A10: Growing ginger at home is relatively easy:
- Choose a rhizome: Select a fresh ginger rhizome with small buds.
- Plant the rhizome: Plant it in a pot with well-draining soil, with the buds facing up.
- Water and light: Keep the soil moist and place the pot in a warm, partially shaded area.
- Harvest: Ginger can be harvested after about 8-10 months when the leaves start to yellow.
These FAQs should provide a comprehensive overview of ginger, covering its uses, benefits, and practical tips for handling and growing it.