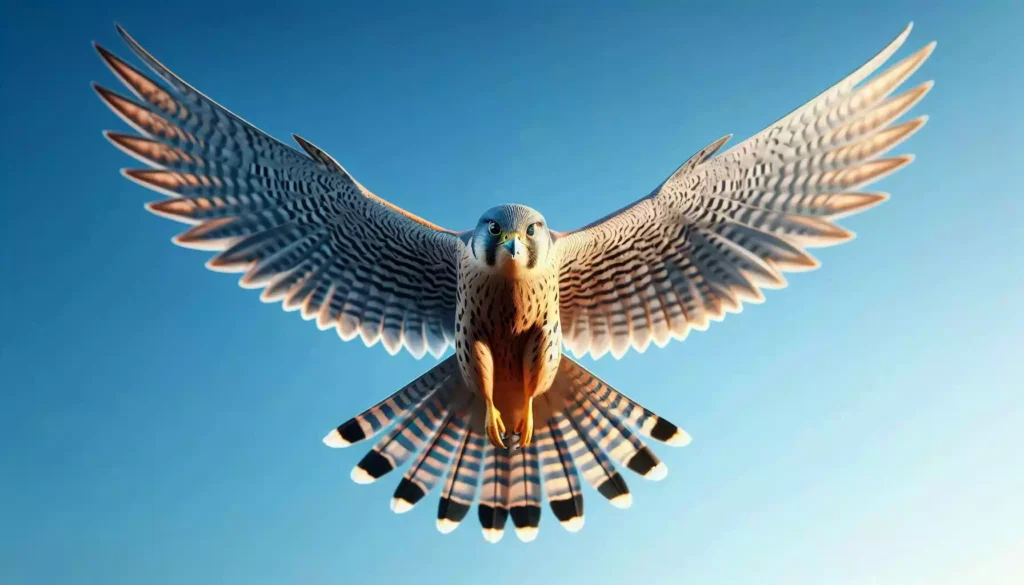
The peregrine falcon, one of the most widespread and awe-inspiring birds of prey, has captivated the human imagination for centuries. Known for its unparalleled speed and agility, this raptor is a testament to the wonders of natural evolution. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the peregrine falcon, exploring its physical characteristics, hunting prowess, conservation status, and its significance in human culture.
Physical Characteristics
The peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus) is a medium-sized bird of prey, with a robust build and distinctive markings. Adult peregrines typically measure between 34 to 58 centimeters in length, with a wingspan ranging from 74 to 120 centimeters. Males are generally smaller than females, a common trait in raptors known as sexual dimorphism.
- Plumage: The peregrine falcon’s plumage is a striking combination of dark blue-gray on the back and wings, with a white or buff-colored underside. The head is adorned with a black cap, and the cheeks are marked with a distinctive black mustache or malar stripe.
- Eyes and Beak: The eyes are dark and piercing, and the beak is sharp and hooked, perfectly adapted for tearing flesh.
- Feet: The peregrine’s feet are equipped with powerful talons, which are crucial for capturing and holding prey.
Hunting Prowess
The peregrine falcon is renowned for its hunting skills, particularly its ability to dive at breathtaking speeds. This maneuver, known as a stoop, is a testament to the falcon’s aerodynamic perfection.
- Stooping: During a stoop, the peregrine folds its wings and tucks its feet, reducing air resistance and allowing it to reach speeds of up to 320 kilometers per hour. This makes the peregrine the fastest animal on Earth.
- Prey Selection: Peregrines primarily hunt other birds, including pigeons, doves, ducks, and smaller songbirds. They are also known to take small mammals and occasionally insects.
- Hunting Technique: The peregrine typically spots its prey from a high vantage point, such as a cliff or tall building. It then initiates a stoop, striking its prey with a powerful blow from its talons, often killing it instantly.
Habitat and Distribution
Peregrine falcons are found on every continent except Antarctica, making them one of the most widely distributed birds of prey. They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of habitats, from deserts and tundra to urban environments.
- Natural Habitats: In the wild, peregrines prefer open areas with cliffs or tall trees, which provide suitable nesting sites and vantage points for hunting.
- Urban Adaptation: In recent years, peregrines have successfully colonized urban areas, nesting on tall buildings and bridges. These structures mimic the natural cliffs they typically use for nesting, and the abundance of pigeons and other urban birds provides a reliable food source.
Conservation Status
The peregrine falcon has faced significant challenges over the years, but conservation efforts have led to a remarkable recovery.
- Historical Decline: In the mid-20th century, peregrine populations plummeted due to the widespread use of DDT, a pesticide that caused thinning of eggshells and led to widespread reproductive failure.
- Recovery Efforts: In the 1970s, DDT was banned in many countries, and conservation programs were initiated to protect and restore peregrine populations. These efforts included captive breeding and release programs, as well as the installation of artificial nesting boxes in urban areas.
- Current Status: Today, the peregrine falcon is no longer considered endangered, and its populations are stable or increasing in many parts of the world. However, ongoing threats such as habitat loss, pollution, and climate change continue to pose challenges.
Cultural Significance
The peregrine falcon has played a significant role in human culture, particularly in the art of falconry.
- Falconry: For centuries, peregrines have been used in falconry, a traditional hunting practice that involves training birds of prey to hunt game. Falconry is still practiced in many parts of the world and is recognized by UNESCO as an intangible cultural heritage.
- Symbolism: The peregrine falcon is often associated with speed, power, and freedom. It has been featured in literature, art, and mythology, symbolizing the wild and untamed aspects of nature.
- Conservation Awareness: The peregrine’s recovery from near extinction has become a symbol of successful conservation efforts, inspiring hope and action for the protection of other endangered species.
Conclusion
The peregrine falcon is a remarkable bird, embodying the beauty and complexity of the natural world. Its ability to adapt to diverse environments, coupled with its incredible hunting skills, makes it a true marvel of nature. As we continue to face environmental challenges, the story of the peregrine falcon serves as a reminder of the resilience of wildlife and the importance of conservation efforts in preserving the natural world for future generations.
Table: Key Facts About the Peregrine Falcon
| Category | Details |
| Scientific Name | Falco peregrinus |
| Size | Length: 34-58 cm, Wingspan: 74-120 cm |
| Weight | Males: 330-1000 g, Females: 700-1500 g |
| Plumage | Dark blue-gray back, white or buff underside, black cap, and black malar stripe |
| Habitat | Cliffs, tall buildings, urban areas, deserts, tundra |
| Diet | Primarily birds, occasionally small mammals and insects |
| Hunting Speed | Up to 320 km/h during a stoop |
| Conservation | No longer endangered, populations stable or increasing |
| Cultural Role | Falconry, symbol of speed and power, featured in literature and art |
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the peregrine falcon, highlighting its unique characteristics and the ongoing efforts to protect this magnificent bird.
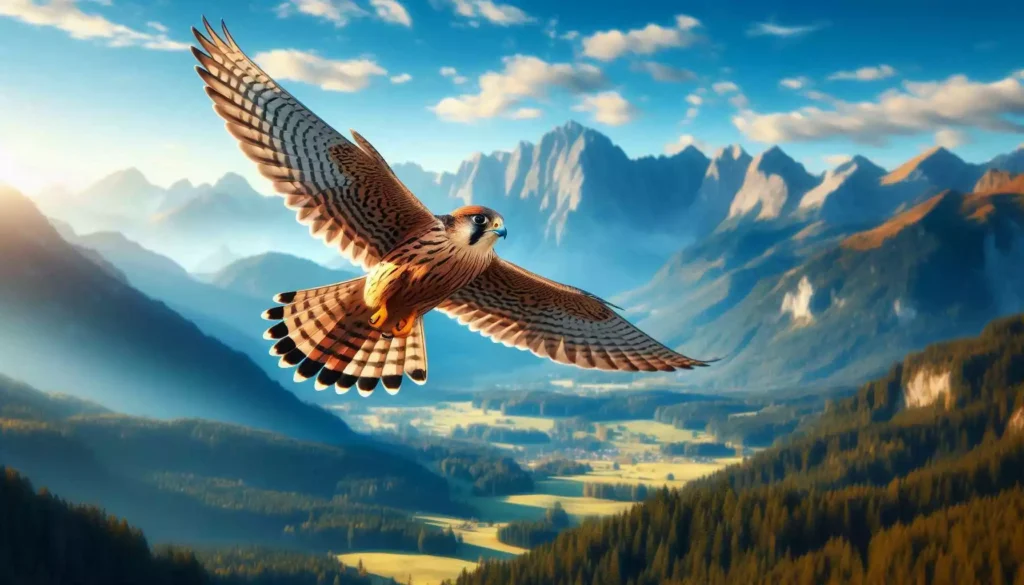

Certainly! Below are some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Peregrine Falcon, one of nature’s most majestic and awe-inspiring birds of prey:
1. What is a Peregrine Falcon?
Answer: The Peregrine Falcon, scientifically known as Falco peregrinus, is a large, powerful bird of prey known for its incredible speed and agility. It is one of the most widespread birds in the world, found on every continent except Antarctica.
2. How fast can a Peregrine Falcon fly?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons are renowned for their speed. During a hunting dive, called a “stoop,” they can reach speeds of up to 240 miles per hour (386 kilometers per hour), making them the fastest animals on Earth.
3. What does a Peregrine Falcon look like?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons have a distinctive appearance. They are typically 14 to 20 inches (36 to 50 cm) in length, with a wingspan of 33 to 44 inches (84 to 112 cm). They have a blue-gray back, barred white underparts, and a dark head with a black “mustache” or cheek stripe. Their eyes are dark, and they have a hooked beak and sharp talons.
4. Where do Peregrine Falcons live?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons are highly adaptable and can be found in a variety of habitats, including urban areas, coastal regions, and mountainous regions. They are known to nest on cliffs, tall buildings, and even bridges, where they can have a clear view of their surroundings.
5. What do Peregrine Falcons eat?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons are primarily bird hunters, preying on a wide range of birds, including pigeons, doves, ducks, and even smaller raptors. They are also known to catch bats and other small mammals. They typically hunt by diving from great heights, using their speed and agility to catch their prey mid-air.
6. How do Peregrine Falcons catch their prey?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons use a hunting technique called a “stoop,” where they dive from high altitudes, reaching incredible speeds. They tuck their wings and tail in, reducing air resistance, and use their powerful talons to strike and capture their prey. Once they have caught their prey, they may either eat it on the spot or carry it to a perch to consume it.
7. How do Peregrine Falcons reproduce?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons typically mate for life. They begin breeding at around 2-3 years of age. The female lays 3-4 eggs, which are incubated for about 33 days. Both parents take turns incubating the eggs and caring for the chicks, which fledge (leave the nest) at around 6 weeks of age.
8. Are Peregrine Falcons endangered?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons were once endangered due to the widespread use of the pesticide DDT, which caused their eggshells to thin and break. However, conservation efforts, including the banning of DDT and the implementation of recovery programs, have helped their populations recover. Today, they are considered a species of least concern, but they are still protected in many regions.
9. How do Peregrine Falcons adapt to urban environments?
Answer: Peregrine Falcons have successfully adapted to urban environments, where they can find tall buildings that mimic their natural cliff habitats. These buildings provide excellent vantage points for hunting and nesting. Urban Peregrines often prey on city birds like pigeons and starlings, and they have become a common sight in many cities around the world.
10. What is the cultural significance of the Peregrine Falcon?
Answer: The Peregrine Falcon has been revered in many cultures throughout history. In medieval times, it was a prized bird for falconry, a sport where trained falcons were used to hunt game. Today, the Peregrine Falcon is a symbol of strength, speed, and grace, and it is often featured in literature, art, and even as a mascot for sports teams.
11. How do researchers study Peregrine Falcons?
Answer: Researchers use various methods to study Peregrine Falcons, including satellite tracking, banding, and nest monitoring. Satellite tracking allows scientists to follow the movements of individual falcons over long distances, while banding involves placing a unique identifier on the falcon’s leg to track its movements and lifespan. Nest monitoring helps researchers understand breeding behaviors and the health of the population.
12. Can Peregrine Falcons be kept as pets?
Answer: In most countries, it is illegal to keep Peregrine Falcons as pets without the proper permits and licenses. These birds are protected by wildlife laws, and their ownership is strictly regulated to ensure their conservation and welfare. Only experienced falconers with the necessary training and permits are allowed to keep and train Peregrine Falcons.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of the Peregrine Falcon, highlighting its unique characteristics, behaviors, and the efforts to protect this magnificent bird.